If you’re considering starting an ecommerce business, you may want to use the wholesale business model. It’s an approach that involves purchasing and reselling products at retail.
By the end of this article, you’ll know about both types of wholesaling businesses that use this approach to sell goods.
Wholesale Definition
Wholesale refers to one of two approaches to business:
A business may purchase goods directly from manufacturers, store them in a warehouse, and then resell them. These are known as warehouse businesses.
Wholesale can also refer to small businesses that make their own products and sell them to suppliers. The suppliers then sell the products to the end-user or the retail customer. These are known as wholesale suppliers.
What is a Wholesale Business?
A wholesale business is built on selling products in bulk to another retailer. The wholesale price is discounted enough that you can still make a profit. The retailer businesses then put the products in their retail stores with a markup. That markup is where their profit comes from. That price is known as the retail price.
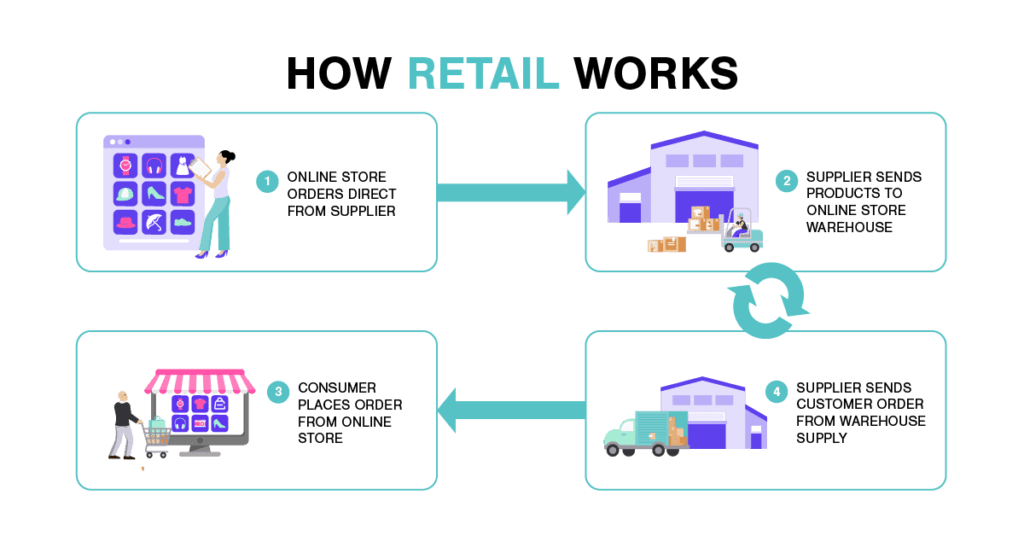
As a wholesaler, you create a channel that sells to retail businesses that then sell to consumers. Selling large quantities of goods ensures you make money whether the retailer sells the inventory or not. It reduces your handling time and costs.
If you’re wholesaling a product you developed, you can still sell your products directly to consumers, too.
For example, if you create a private label product, you can sell it to other retailers at a wholesale price to get your product in more stores. Then, you can still sell that product directly to consumers on your website, at retail.
Types of Wholesale
The wholesale industry can be rather complex to navigate. Some wholesalers opt to work independently. Others choose to work with one or two producers. Wholesale businesses fall into one of three categories:
Merchant Wholesalers
This arrangement is the most common. Merchant wholesalers don’t manufacture their own products. Instead, they purchase large volumes of products. They sell in smaller amounts at a higher price point. Even though they don’t sell their own products, they have extensive knowledge of products. They know the right time to start selling to retail businesses across varying industries.
Brokers
Brokers are middlemen between the wholesale operator and their clients. Brokers generally do not own the products they sell. Brokers earn their money by negotiating deals between the two parties. They get a sales commission.
Sales and Distribution
Manufacturers reach out to wholesale operators to offer products. Rather than relying on wholesale businesses finding a manufacturer, manufacturers hire people to represent them to wholesalers. This approach creates wholesale deals customized to each individual case.
Benefits of Wholesale
If you want to open an online store, a wholesale business may be the way to go.
Save Money
Buying a large volume of products or large quantities of a single product helps you save money. You’ll usually get a discount, known as wholesale pricing. The wholesale prices make it easier for you to profit since the retail price is always higher.
Think of it like this. If you use a retail arbitrage business model, you’re already paying retail. Unless you get products on clearance, it’s hard to make a profit. Customers aren’t often willing to pay more than the retail price for something.
Build a Strong Supplier Network
Those who wholesale products from a variety of companies need a solid network of manufacturers and suppliers. For your business to succeed, you must have quality products delivered on time.
When you’re just getting started, it can be challenging to establish your supply chain. But as you continue to work with suppliers, you’ll be able to foster a strong relationship. Maintaining your relationships and working to keep them positive will pay off. Your brand will establish itself as reliable and sustainable.
Establish Expertise
You’ll conduct a lot of market research about the products you want to sell. It doesn’t matter whether you’re selling car parts, party supplies, jewelry, or something else entirely. You’ll end up with an edge that your customers will learn to trust.
Easy to Expand
After you’ve established yourself in the industry, you can make connections with other markets. You may find cross-selling and upselling opportunities that help you grow your business faster.
The expansion itself will be easy since you already have an established brand and established relationships. Anything new you add will be much easier and faster than your business’s initial setup.
Disadvantages of Wholesale
Wholesalers cannot be as responsive to changing market conditions. Retailers are at the front of the line, building relationships with consumers. Wholesalers have to rely on feedback from retailers, as well as research to maintain their competitive advantage.
Difficult to Retain a Brand Identity
Wholesalers trust products to retailers. As such, they must rely on the retailer to retain the product’s brand identity. The last thing you want is to supply a product to Target and for customers to think it’s a Target product.
As a wholesaler, it’s not always possible to control the way your product is merchandised. You won’t have control over the pricing they set or what products they display around it.
Marketing Can Be a Challenge
In the wholesale business, you are still responsible for marketing your product to consumers. You can’t expect that retailers will do all the work.
By handling the marketing yourself, you can support consistency in the messaging, brand identity, and product placement. You can’t expect each retailer to market the products the way they want to while still having any kind of consistency in your messaging.
Retailers have to be able to find you. There are tons of online stores out there offering their products, so you have to stand out. It won’t do you any good to have a better price than your competition, have great product lines or simple distribution channels if no one knows about it.
You Must Have Ample Warehouse Space
Because you’ll have such a large inventory, you’ll need a place to store the items until you sell them. If you don’t have a warehouse, you’ll need to rent one.
Beyond the warehouse space itself, you also needed to have solid, streamlined warehouse processes. If picking and packing aren’t organized and efficient, you’ll find yourself with a customer service issue.
If you ship products, but they are what someone ordered, it’s a mistake you’ll have to fix. And that kind of mistake costs money. If it happens occasionally, it’s not that big of a deal. But if it happens often, you’ll not only risk losing customers, but you’ll find that you’re wasting a ton of money unnecessarily.
Your warehouse inventory should seamlessly integrate with your wholesale management platform. This way, you always know how many of each item is in your warehouse. You know what you need to order more of and exactly where you’re going to put it.
Inventory and Capital Risk
After you purchase the inventory from the supplier, it’s yours. That means if you don’t sell it, you’re stuck with it.
And even though you’re not paying as much per piece as you would with retail pricing, you’re still spending a lot of money. Wholesale products require bulk, which means you’ll still pay thousands of dollars for a decent inventory.
Distributor vs. Wholesale vs. Retail
Products have a lot of ground to cover before they ever make it to the final customer. Wholesalers, distributors, and retailers are all part of the supply chain that takes a product from the manufacturer to the end customer.
Distributors
A distributor is an independent entity that enters an agreement with a manufacturer to sell its products to wholesalers and retailers. Distributors aren’t generally allowed to sell competing products or other product lines. However, the terms of the agreement vary from one industry to the next. Distributors can often negotiate the terms of their contracts with manufacturers to create something mutually beneficial.
Generally, distributors carry large amounts of stock. They have the warehouse space to store goods for up to 12 months. When a new potential buyer approaches a manufacturer, they have to deal with the chosen distributor as their main point of contact.
Wholesalers
A wholesaler is someone who makes a bulk purchase from a distributor and then sellers it to a retailer. Wholesalers generally specialize in a particular product, for instance, men’s shoes. Alternatively, they opt to carry a wide range of stock for retailers across a variety of industries. Wholesalers who do not stock competing products are considered distributors.
Beyond breaking bulk orders down into smaller quantities, wholesalers may also opt to assemble goods. Wholesalers don’t generally store products as long as distributors do. They hold products for up to six months at a time.
Retailers
These are for-profit businesses (Amazon, Walmart, Target, etc.) that sell products and services direct to consumers. The products are intended for use rather than resale.
To generate a profit, the retailer has to find a wholesaler or distributor who sells the products at the right price and quantity. Then the retailer marks up the price to cover their expenses and make a profit.
Each product may have a different profit margin, but the markup is intended to cover everything from advertising costs to rent and employee salaries.
Retailers can run online stores or brick-and-mortar stores. Some opt for both. They sell their products across multiple sales channels, including online marketplaces.
How to Find Wholesale Products to Sell
If you want to open an ecommerce store, you need products to sell. There are several ways to do this:
Contact Manufacturers Directly
If you plan on selling branded items, approach the manufacturer directly. Find out more about the minimum order requirements. If they only use an established distribution channel, get a list of distributors to contact.
The fewer channels you have to go through, the lower your costs. This not only allows you to make more money but to be more competitive in the marketplace.
Explore a Wholesale Marketplace
Sites like Alibaba and AliExpress make it easy to find products and research suppliers at once. When you find a product you want to buy, check out the wholesale supplier who offers it. Other wholesalers may provide the same products at the same price. Make sure you take a look at their reputation, lead time, shipping costs, etc.
Join Industry Groups
Many small business owners come together in groups. They’re a great source of information. Take time to build your network and get to know people. If you’re in direct competition with them, don’t be surprised if they don’t want to share much with you.
Attend Trade Shows
Trade shows are events designed specifically to connect distributors and manufacturers to retailers. You can meet multiple wholesalers and manufacturers throughout the day. Face-to-face communication can help you connect in ways that online communication cannot.
Spend time browsing the Trade Show News Network. It’s the largest online directory of trade shows. You’ll be able to find trade shows based on date, location, industry, or event name.
Wholesale vs. Dropshipping
Dropshipping is a business model where a retailer doesn’t keep stock. Wholesalers keep stock and sell it to retailers. The drop shipper earns a commission on orders transferred to the wholesaler.
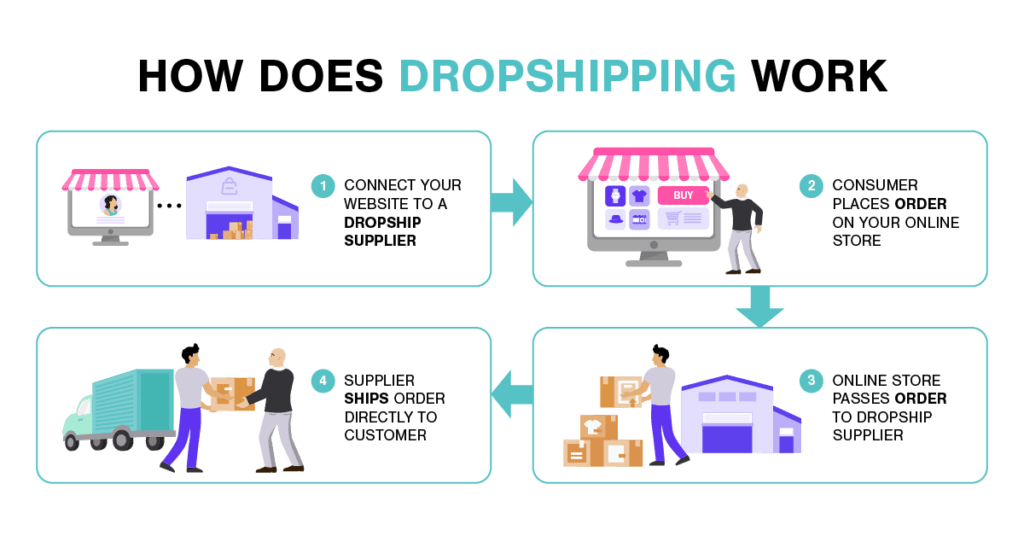
As a drop shipper, when you receive a new order, you send it to your wholesale partner, who then ships it to your customer. The wholesaler takes a commission from that.
Retail stores that operate on the dropshipping model heavily rely on wholesale suppliers. Drop shippers must be strategic about choosing the right partner.
Both businesses work well but are meant for different entrepreneurs. As a wholesaler, you could easily work with several drop shippers.
Retail Markup: How Much Profit?
The retail markup is the difference between the cost of a product and the selling price. There is no universal amount or percentage that works across all products. Each product you find will likely have a suggested retail price. It’s up to the retailer to use that as a guide.
Retail Markup = Sales price – Cost
Retail Markup Percentage = Markup Amount / Retail Selling Price
For example, if a product unit costs $5 and the retail price is $10, then the markup is $5. The markup percentage is 50%.
In an industry where costs are consistent and generally low, the markup will be low, too. Grocery stores, for instance, have a markup of 15% or less.
But not all food industries sell products the same way. Restaurants, for instance, typically mark up meals by about 60%. Some drinks may have up to a 500% markup.
When you consider that restaurants have a high overhead, the profit margins are still low. Restaurants average less than 5% profit, with fast food averaging even less.
Jewelry is usually marked up 50%, with clothing marked up as much as 300%. And we’re not just talking about high-end fashion designer brands.
Smartphones only have a markup of about 10%. The industry makes money on usage fees and service contracts. The costs involved will always dictate how much a retailer selling products can make.
You have to consider industry markups when you choose your niche. That said, you don’t want to choose the clothing niche based on its high markup alone.
Is Wholesaling Right for You?
Selling wholesale means, you’ll need to buy an item (or several different items) in bulk. Suppliers will have minimums in each order. Depending on the product, your minimum order amount may be a certain number of merchandise units. Or, it may be a certain dollar amount.
If you can’t afford the capital required for wholesale buying, then it’s likely not right for you. It’s the significant discount on each piece that makes a small business profitable.
If you want to sell to the end customer who will use the product or service, you want a retail business model.
In either case, you can build your own online store that sells products and earns a profit.









